Indigenous Governance Database
data sovereignty
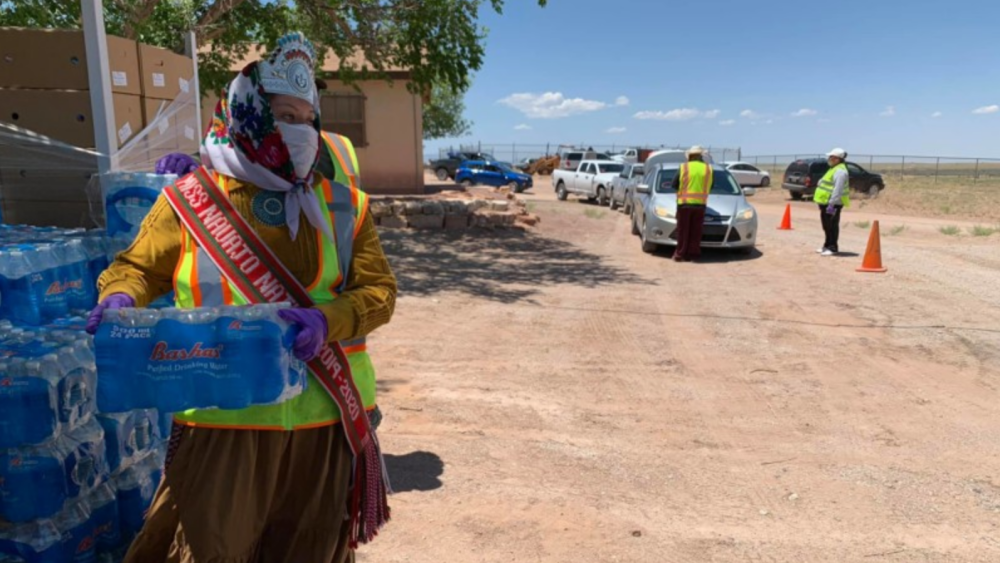

Indigenous Data in the Covid-19 Pandemic: Straddling Erasure, Terrorism, and Sovereignty
On April 10, 2020, Covid-19 case rates on tribal lands were more than four times the rate in the United States.1 Indigenous Peoples across the country continue to be disproportionately impacted by the coronavirus. As of May 18, 2020, the Navajo Nation has the highest Covid-19 case rates surpassing…
Indigenous Data Sovereignty: The CARE Principles and the Biocultural Labels Initiative
The NYU Alliance for Public Interest Technology Alliance is a dynamic and multidisciplinary group of NYU faculty who are experts on the responsible and ethical creation, use and governance of technology in society. The Alliance is a provostial initiative that connects numerous NYU hubs and…

Policy Brief: Indigenous Data Sovereignty in Arizona: Setting an Agenda
Indigenous data sovereignty asserts the rights of Native nations and Indigenous Peoples to govern the collection, ownership, and application of their own data. Indigenous data sovereignty derives from tribes’ inherent right to govern their peoples, lands, and resources. In the United States and…

Policy Brief: Supporting Tribal Data Governance for Indigenous Community Climate Resilience
Tribal communities have the right to define, collect, protect, interpret, manage, and apply data in a way that respects Indigenous ethics, values, and relational responsibilities. These rights are critically relevant in the context of increasing climate impacts, where Indigenous communities need…

Principles of Indigenous Data Governance
Indigenous data, whether collected by national governments and institutions or gathered by Indigenous Peoples themselves, are integral for: decision-making; the exercise of collective rights to self-determination; the affirmation and application of Indigenous epistemologies; and fulfilling…

Access and Management: Indigenous Perspectives on Genomic Data Sharing
As genomic researchers are encouraged to engage in broad genomic data sharing, American Indian/Alaska Native/Native Hawaiian (AI/AN/NH) leaders have raised questions about ownership of data and biospecimens and concerns over emerging challenges and potential threats to tribal sovereignty. Using a…

CARE Principles for Indigenous Data Governance
Los Principios CREA para la Gobernanza de Datos Indigenas The increasing convergence of technology infrastructure and digital connectivity has raised the value of data across the globe. Whether existing knowledge is digitised or new data are ‘born digital’, the impact they have on decision-making,…

Tribal Data Governance and Informational Privacy: Constructing "Indigenous Data Sovereignty"
There is a growing movement among Indigenous peoples to assert aright to “Indigenous data sovereignty,” and yet, the term “data sovereignty” is not widely understood. What does it mean to control the collection, useand management of information in an era of “Big Data,” in which digital technology…

Issues in Open Data: Indigenous Data Sovereignty
Open data in the context of Indigenous peoples is a double-edged sword. Open data is a site of tension for Indigenous peoples. Open data provides opportunities for sustainable development according to Indigenous aspirations, yet also sits at the nexus of current and historic data challenges as a…
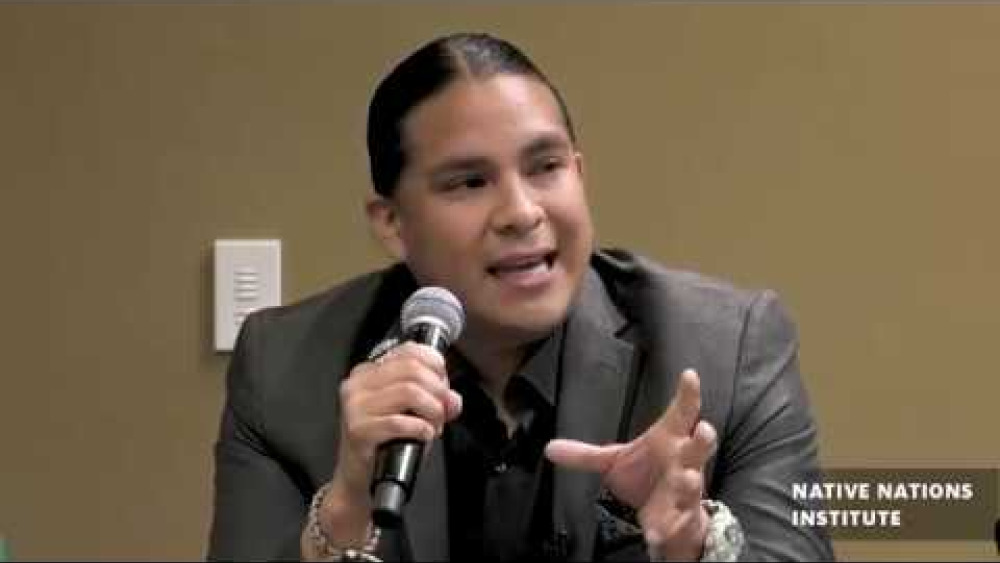

Indigenous Data Sovereignty Panel IDSOV Summit Arizona 2019
Native scholars working to advance the research on indigenous data sovereignty give their perspectives on the issues facing Native communities around data collection and date use. Dr. Jameson D. Lopez (Fort Yuma Quechan (Kwatsáan) Indian Tribe), Carmenlita Chief (Navajo Nation), and Dr. Tennille…

Genomic Research Through an Indigenous Lens: Understanding the Expectations
Indigenous scholars are leading initiatives to improve access to genetic and genomic research and health care based on their unique cultural contexts and within sovereign-based governance models created and accepted by their peoples. In the past, Indigenous peoples’ engagement with genomic research…

Good Data Practices for Indigenous Data Sovereignty
Indigenous Data Sovereignty (IDS) and Indigenous Data Governance are Indigenous-led movements and practices through which Indigenous peoples are setting their own visions for good data regarding data generated and collected by and about them. IDS movements and practices can be seen as a…

Indigenous Data Sovereignty: Global Progression
On May 18, 2018 at the Native American and Indigenous Studies Association (NAISA) Conference in Los Angeles, six leading scholars discussed the landscape and global opportunities and challenges Indigenous peoples face in the growing Indigenous data sovereignty movement. The presentations provided…

Policy Brief: Indigenous Data Sovereignty in the United States
We live in the information age. Governments, industries, and organizations of all kinds are claiming a right to gather information on everything from our spending habits to our health records. Data has become a global currency, a valuable asset, and a source of power. Native nations are part of…

Policy Brief: Data Governance for Native Nation Rebuilding
Native nations in the United States are increasingly exercising Indigenous data sovereignty (ID-Sov)— the right of a nation to govern the collection, ownership, and application of its own data. While ID-Sov is the goal, data governance— the ownership, collection, control, analysis, and use of data…

Data as a Strategic Resource: Self-determination, Governance , and the Data Challenge for Indigenous Nations in the United States
Data about Indigenous populations in the United States are inconsistent and irrelevant. Federal and state governments and researchers direct most collection, analysis, and use of data about U.S. Indigenous populations. Indigenous Peoples’ justified mistrust further complicates the collection and…

Eileen Briggs: The Importance of Data and Community Engagement
Eileen Briggs is a citizen of the Cheyenne River Sioux Tribe and is the Executive Director of Cheyenne River Sioux Tribal Ventures. She is also the Principal Investigator on "Cheyenne River Voices Research" — a reservation-wide research project including a household survey of over 800 families that…
