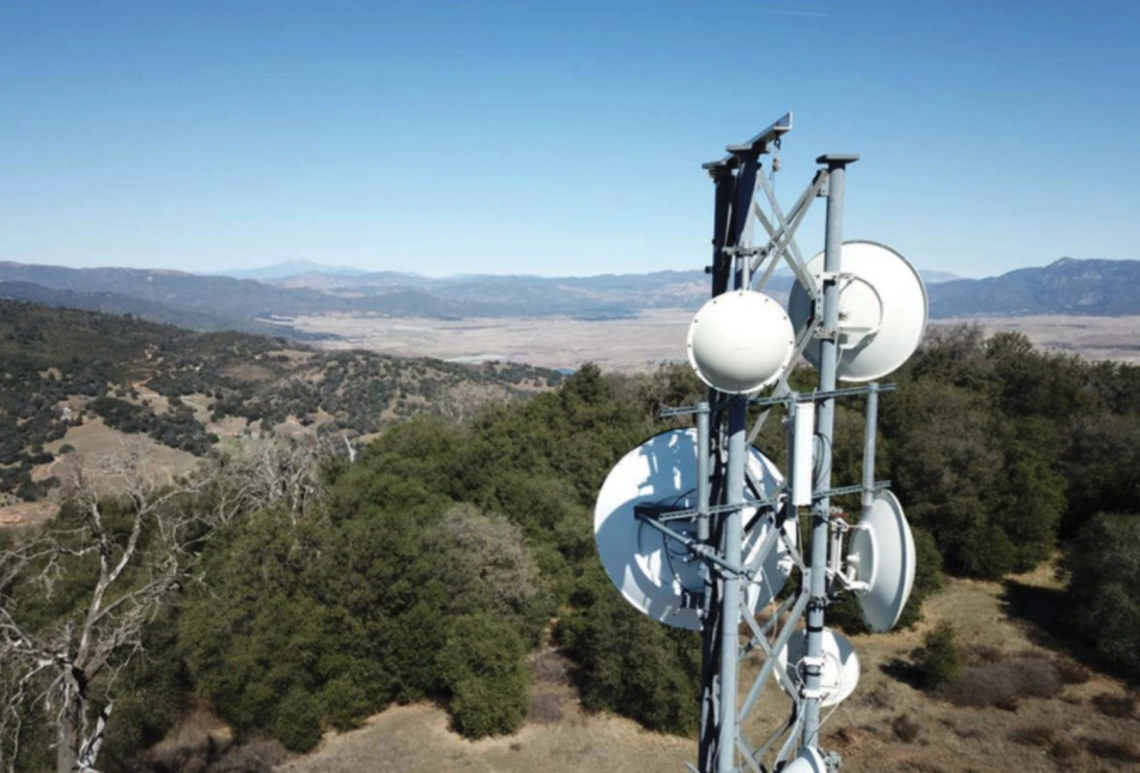
Access to high-speed Internet service has become an essential component to the nation’s economy, education, and healthcare. However, federal data continues to show tribal lands are the least connected areas of the country. AIPI launched a survey to collect information from residents of tribal reservations to determine what levels of Internet access they had and what types of devices they using to access it. The study also identified potential barriers to access, such as the lack of availability or its unaffordability for residents to purchase.
Our survey found that residents on tribal lands are predominantly using smartphones to access the internet, while many are also accessing it through public Wi-Fi or at a friend/relative’s house. However, the data should not be interpreted or used to defend “mobile only” as the singular solution to providing internet service. In this study 50% of respondents stated that their internet use was limited because they did not have enough data in their cell phone plan. Further research is needed to ascertain if there are specific limitations of mobile use in certain situations, such as the reliability or preference of using mobile over hardline connections for certain activities.
Additional Information
Howard, Brian and Morris, Traci, Tribal Technology Assessment: The State of Internet Service on Tribal Lands (July 27, 2019).