Contemporary debates about poverty and its mitigation often invoke the idea of social inclusion: the effort to increase the capacities and opportunities of disadvantaged populations to participate more fully in the economy, polity, and institutions of developed societies. While practical outcomes have been inconsistent, this idea has been prominent in the social policies of both Canada and the United States. Both generally see themselves as liberal democracies committed to building socially inclusive societies, and both have adopted policies in support of that goal. However, we argue in this article that social inclusion, as presently conceived, fails to comprehend or address the distinctive situation of Indigenous peoples in both of these countries. Our critique focuses on four aspects of social inclusion as applied to Indigenous peoples: the external conception of needs, the individualization of both problems and solutions, the favoring of distributional politics over positional politics, and the conditionality of inclusion. We argue that both Canada and the United States need to reconceive social inclusion in ways that address these issues and that a more capacious conception of federalism may hold the key.
Indigenous Governance Database
What are the Limits of Social Inclusion? Indigenous Peoples and Indigenous Governance in Canada and the United States
Related Resources

Progressing Issues of Social Importance Through the Work of Indigenous Artists: A Social Impact Evaluation of the Native Arts and Cultures Foundation’s Pilot Community Inspiration Program
In 2014, the Native Arts and Cultures Foundation (NACF) launched a new initiative, the Community Inspiration Program (CIP), which is rooted in the understanding that arts and cultures projects have an important role to play in motivating community engagement and supporting social change. This…
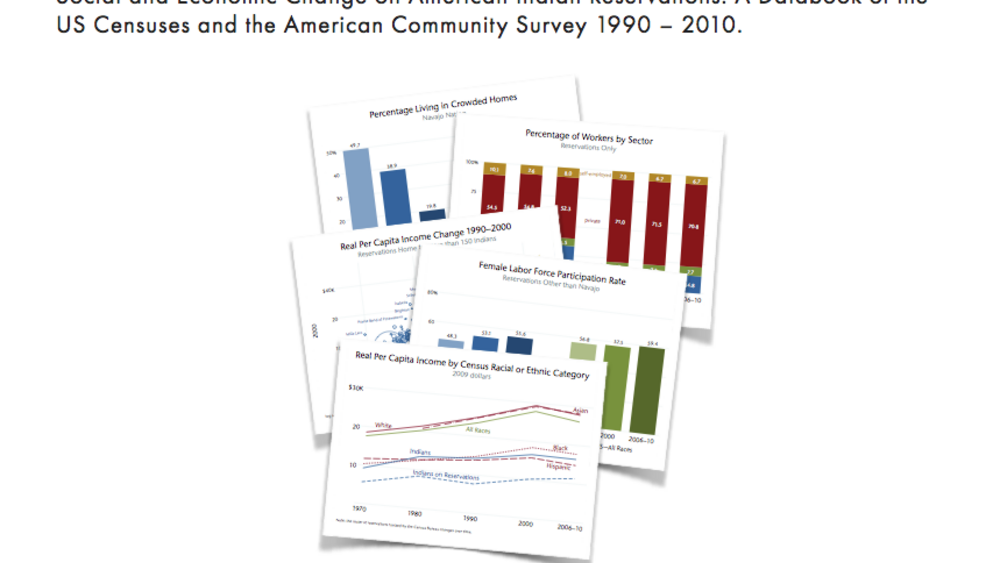
Social and Economic Change on American Indian Reservations: A Databook of the US Censuses and the American Community Survey 1990-2010
The fortunes of Indians on reservations continue to lag those of other racial and ethnic groups tracked by the census in the United States. The per capita income of Indians on reservations, for example, has been less than half the US average, consistently falling far below that of Hispanics,…
![Tribal Law as Indigenous Social Reality and Separate Consciousness: [Re]Incorporating Customs and Traditions into Tribal Law Tribal Law as Indigenous Social Reality and Separate Consciousness: [Re]Incorporating Customs and Traditions into Tribal Law](/sites/default/files/styles/resources/public/resources/Screen%2520Shot%25202016-10-11%2520at%25201.22.13%2520PM.png?itok=pvkjKhR1)
Tribal Law as Indigenous Social Reality and Separate Consciousness: [Re]Incorporating Customs and Traditions into Tribal Law
At some point in my legal career, I recall becoming increasingly uncomfortable with the inconsistencies between the values in the written law of various indigenous nations and the values I knew were embedded in indigenous societies themselves. The two are not entirely in harmony, and in fact, in…

